您想继续阅读英文文章还
是切换到中文?
是切换到中文?

THINK ALUMINIUM THINK AL CIRCLE

In a novel breakthrough, University of California scientists have developed a special aluminium alloy that produces hydrogen at room temperature by reacting with water. Aluminium is a reactive material that already separates oxygen from water molecules, leaving hydrogen behind. According to Santa Cruz Works, the novel aluminium nanoparticles combine with water to produce hydrogen at room temperature.
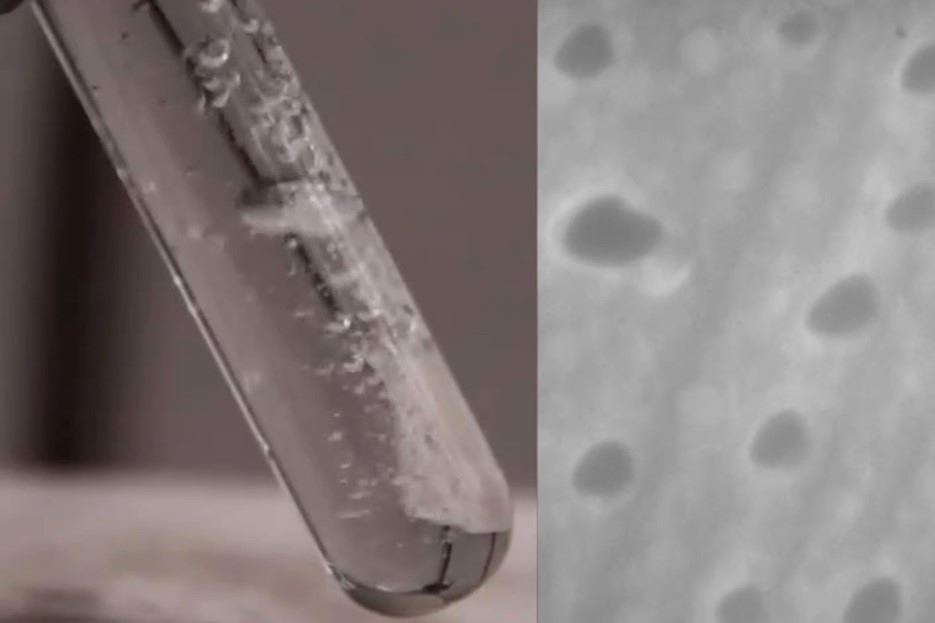
Aluminium is a very reactive material that produces hydrogen by absorbing oxygen from water molecules. Even though aluminium has a strong affinity with air and forms a protective aluminium oxide layer when it comes into contact with water, it is frequently used in water-based devices due to its quick reaction and lack of risk.
The new study uses affordable gallium and aluminium alloy to make the aluminium nanoparticles, which react fast with water at room temperature to release significant quantities of hydrogen. According to the study, gallium is still easily retrieved for further use from the reaction, which yields 90 per cent of the hydrogen that could have theoretically been created from the response of all the aluminium in the composite.

“We don’t need any energy input, and it bubbles hydrogen like crazy. I’ve never seen anything like it,” said Scott Oliver, a chemistry professor from University of Columbia Santa Cruz.
It has long been understood that this aluminium-gallium combination generates hydrogen. But the UCSC team discovered that when gallium content in the composite grew, so did hydrogen generation. The drawback is that gallium is quite expensive, even if it may be recovered and used repeatedly throughout this procedure. Another disadvantage is that hydrogen fuel cells are still not being adopted widely. Although hydrogen may be used directly as a fuel, doing so can be dangerous, and tanks sometimes need to be under pressure to hold reasonable amounts of hydrogen.
“Our method uses a small amount of aluminum, which ensures it all dissolves into the majority gallium as discrete nanoparticles,” added Oliver. The composite can be made with easily accessible aluminium sources like foil or cans.
Although it may transmit energy, hydrogen itself is not an energy source. But it is seldom discovered in the natural world; instead, it must be created from components that already have it. This particle can store and transfer helpful energy. But none of the resources needed in these industrial techniques—mainly coal, natural gas, or oil are renewable.
Responses








