

Researchers are advancing sustainable practices by optimising electric discharge machining (EDM) processes for aluminium alloys. A recent study highlighted significant improvements in machining efficiency and environmental impact for Al6061 alloys. By employing cryogenically treated brass electrodes and deionised water as the dielectric fluid, the study demonstrated innovative techniques that enhance EDM performance while aligning with sustainability goals.
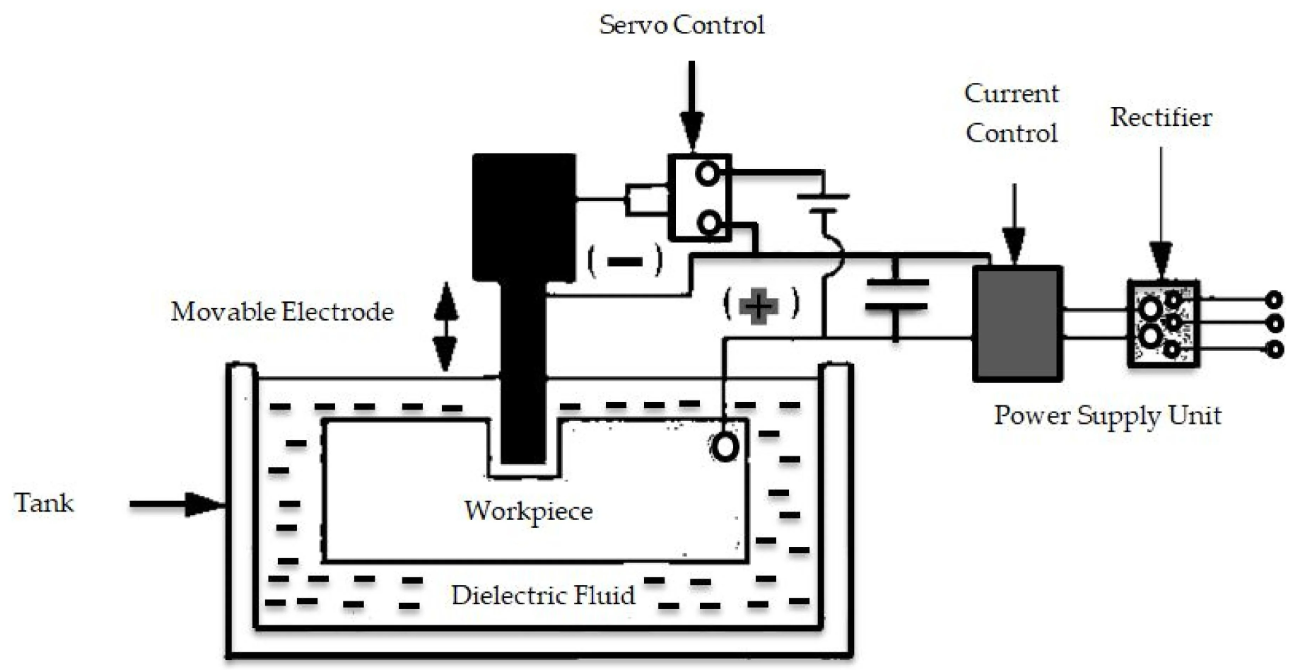 Image Source: MDPI
Image Source: MDPI
EDM has long been valued for its precision in creating complex geometries but faces challenges like low machining rates and environmental concerns associated with traditional dielectric fluids. While kerosene oil is effective, its emissions pose significant environmental risks, highlighting the need for sustainable alternatives. The adoption of deionised water not only mitigates these concerns but also enhances cutting performance considerably.
Electric discharge machining (EDM) is renowned for its ability to produce intricate geometries with exceptional precision. However, it often encounters limitations like low machining rates and environmental drawbacks associated with traditional dielectric fluids. While kerosene oil is effective, its emissions pose significant environmental risks, highlighting the need for sustainable alternatives. The adoption of deionised water not only mitigates these concerns but also enhances cutting performance considerably.
Emergence of sustainable solution & its analysis
Researchers analysed key machining parameters—
The analysis was conducted to assess their impact on material removal rate (MRR), surface roughness (SR), and specific energy consumption (SEC). Using artificial neural networks (ANN) to model these relationships, they aimed to improve predictive accuracy and enhance machining efficiency.
Notably, multi-response optimisation techniques led to significant improvements: a 64.82 per cent increase in MRR, a 27.45 per cent reduction in surface roughness, and a 46.60 per cent decrease in energy consumption. With optimised settings of IP at 24.85 A, SV at 2.18 V, PON at 119.11 µs, and CP at 1.05 g/100 ml, the EDM process achieved remarkable performance gains over unoptimised conditions.
Key finding of the study
A key finding of the study was the effectiveness of cryogenic treatment for brass electrodes, which enhanced material properties and improved machining efficiency. The authors highlighted the impact of multi-response optimisation, stating, - "The magnitudes of MRR, SR, and SEC obtained by multi-response optimisation are 64.82%, 27.45%, and 46.60%, respectively, compared to unoptimised settings."
These results not only demonstrate the effectiveness of sustainable machining methods but also suggest significant cost-saving potential for industries dependent on precision manufacturing.
Beyond its practical applications, this research highlights the growing need for environmentally responsible machining techniques. By reducing harmful emissions, advancements such as deionised water and cryogenic treatment offer a more sustainable approach while maintaining high performance, paving the way for greener manufacturing processes.
Leveraging modelling techniques like - ANN
By leveraging advanced modelling techniques like artificial neural networks (ANN), this study highlights the transformative role of artificial intelligence in manufacturing optimisation, enabling industries to achieve sustainability targets more efficiently.
Overall, the research provides valuable insights into material science and manufacturing engineering, demonstrating how targeted optimisations can significantly improve performance and environmental impact. Future studies can build on these findings by further exploring additional additives and refining machining techniques. The emphasis on sustainability within the EDM framework sets a strong precedent, promoting the adoption of innovative practices across various sectors, particularly those reliant on aluminium alloys and similar materials.



Responses






