

Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have created medical devices that might be employed within the body as stents, staples, or drug depots and then securely broken down on demand when they are no longer required by exploiting a process that causes fractures in the metal.
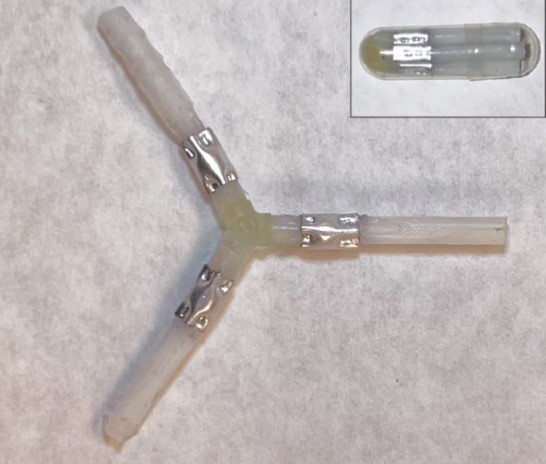
Exposure to eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) can cause aluminium medical devices like stents, staples, or drug depots to dissolve within the body. The researchers wrote about their findings in a recently published report in Advanced Materials. They suggested that this liquid metal alloy may be physically applied to the device or given to patients as nanoparticles.
"It's a really dramatic phenomenon that can be applied to several settings. What this enables, potentially, is the ability to have systems that don't require an intervention such as an endoscopy or surgical procedure for removal of devices," said Giovanni Traverso, the Karl van Tassel Career Development Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT and a gastroenterologist at Brigham and Women's Hospital.
The MIT team was inspired by a phenomenon known as liquid metal embrittlement to develop gadgets that might degrade on demand within the body. This process has received much research as a potential cause of the collapse in metal structures, especially those built of stainless steel and zinc.
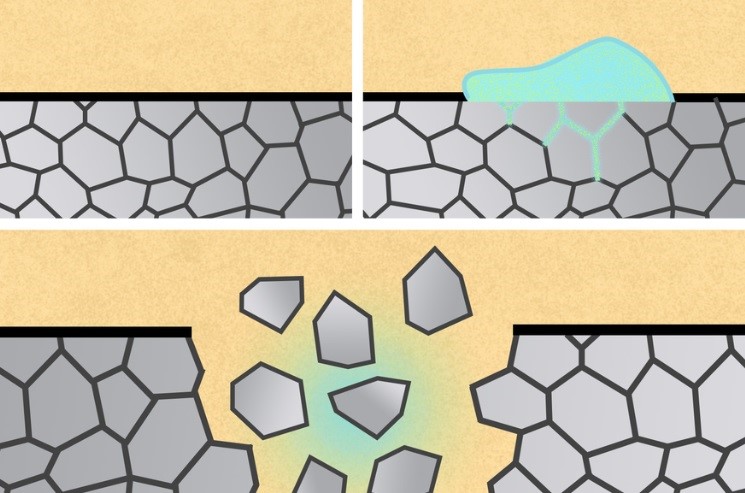
This study aimed to develop devices that could be broken down in the gastrointestinal tract. Still, it soon became apparent that it could also be used to make stents and other biomedical staples.
"It's known that certain combinations of liquid metals can actually get into the grain boundaries of solid metals and cause them to dramatically weaken and fail. We wanted to see if we could harness that known failure mechanism in a productive way to build these biomedical devices," said MIT postdoc Vivian Feig, the paper's lead author.
Additionally, gallium stops aluminium from creating a surface-protective oxide layer, which increases the metal's exposure to water and speeds up the metal's deterioration. The MIT researchers demonstrated that aluminium devices will instantly disintegrate after being sprayed with gallium-indium. Gallium-indium nano- and microparticles were also made by the researchers, and it was shown that these particles, when suspended in a liquid, could disintegrate aluminium structures.
There are two ways that gallium weakens solid metals like aluminium. First, it may diffuse through the metal's grain boundaries or the lines separating the crystals that make up the metal, shattering chunks of the metal. The MIT team demonstrated how they might take advantage of this phenomenon by creating metals with various grain patterns that would allow the metals to fracture or split into little pieces at a specific location.
The scientists also created an aluminium oesophagal stent in addition to metal staples. Currently, medical professionals either leave oesophagal stents within patients when they are no longer required or remove them endoscopically. However, the researchers demonstrated that gallium-indium may be used to disintegrate their aluminium oesophagal stent.
"What this enables, potentially, is the ability to have systems that don't require an intervention such as an endoscopy or surgical procedure for removal of devices," said Giovanni Traverso, the senior author of the study.
Responses








