

Aluminium is a chemical element that was discovered 200 years ago. After an initial period of technological development, aluminium alloys were used in many structural applications, including the civil engineering field. Al is the second most widely specified metal in buildings after steel and is used in all sectors, from commercial buildings to domestic dwellings.

Alloys
Pure aluminium is a low-strength metal and consequently not suitable for building applications, but thanks to the addition of alloying elements such as Cu, Mn, Mg, Zn etc. and thanks to specific production processes, it changes its physical and mechanical properties to meet requirements of a large number of applications.
Durability
Aluminium alloys for buildings are resistant to water, and corrosion and immune to the harmful effects of UV rays, thus ensuring lasting endurance.
Low maintenance costs
Aluminium does not require any special kind of maintenance, whether it is raw or lacquered Al (glaze, finish, lamination and layer).
Finishes
Aluminium can be anodized or lacquered in any colour, so it’s possible to get the most varied effects and thus meet the designer’s decorative needs.
Reflective properties
Aluminium is widely used for light management: its reflective properties help to reduce energy consumption for lighting and heating.
It is possible to reduce the use of air conditioning in the summer season by using aluminium shielding devices. Aluminium does not burn and is, therefore it’s classified as a non-combustible material.
Nevertheless, aluminium alloys melt at about 650°C without releasing harmful gases. And so, more and more often, the outer covers and external surfaces of industrial structures (and not) are made with thin aluminium panel finishes, which are destined to merge only in case of fierce fire, thus allowing heat and smoke to escape and reducing damage caused by the fire.
Benefits of aluminium roofing sheets:

Aluminium in buildings:
Applications of aluminium products in buildings include both structural and non-structural uses. Typical applications are shown in Figure 1. Aluminium in Green Buildings Aluminium metals is generally in alloy forms, whereby aluminium is the predominant metal that is intimately mixed with other elements such as copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin and zinc. Aluminium alloys can be processed into different forms depending on the processing method. Like most other metals, the processing methods involve rolling, casting, forging, drawing, tubing, extrusion, etc. As a result, aluminium products can be categorized into the following types: sheet and plate, foil, extruded products, forged products, wire and cable, casting/foundry products, and paste and powder.

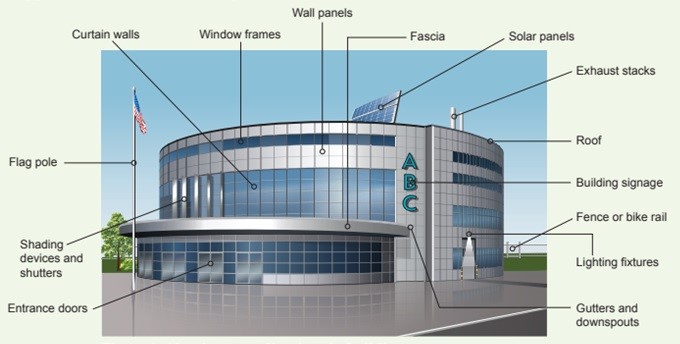
Figure 1: The curtain walls and ventilation ducting shown in this image take advantage of aluminium’s inherent properties: lightweight, strong, flexible, and long-lasting
Certified studies have proved that the aluminium alloys, the surface treatments (coatings) and the materials used are all neutral. Aluminium used in the construction industry does not negatively impact the air quality inside buildings, on land or water.
25% of all aluminium produced worldwide is used in construction. Aluminium is a tool for unlimited creativity in the hands of the architect, making it possible to create structures that cannot be made from wood, plastic, or steel.
Application of aluminium foam in construction:
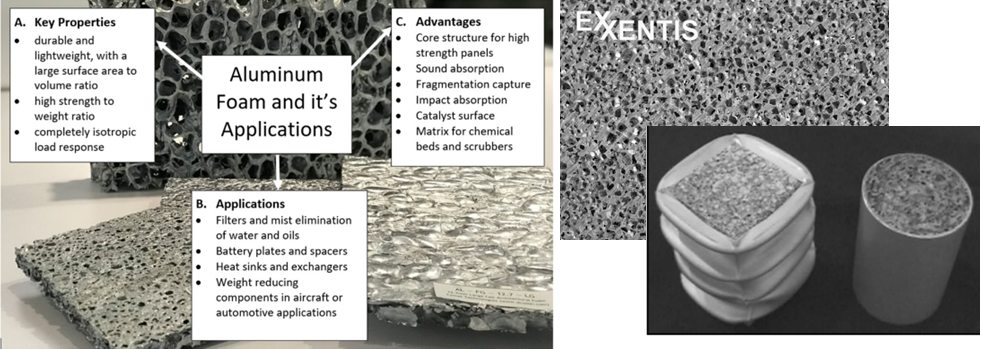
Figure 2: Key properties, applications and advantages of aluminium metallic foam. Prototypes of foam-filled tubes developed as crash absorbers. The tubes are aluminium extrusions filled with aluminium foam. Tube diameter 65 mm. (Photo courtesy of Cymat)
Application of aluminium in electrical conductivity:

Given its electrical conductivity, aluminium extrusion is used in the transmission segment. Aluminium is better than copper in terms of cost and weight. Aluminium is preferred over other materials for use in electricity transmission and distribution. Aluminium extrusions are used by Power Grid, NTPC, GE, Siemens, Schneider, BHEL, ABB, and other customers for several applications such as switch gears, control panels, power substations, etc.
Aluminium wiring is corrosion-resistant and provides twice the conductivity per pound compared to copper wiring. And aluminium wiring requires minimal energy to recycle and loses none of its properties during recycling.

Sustainability of aluminium:

If this were not enough, it is the most common element in the Earth’s crust after oxygen and silicon. On top of this, recycling aluminium requires only 5% of the original energy that the production from virgin raw material would use. Therefore, recycling aluminium reduces by 95% energy consumption compared to its extraction from bauxite, with the environmental advantages that this brings.
A highly durable metal, aluminium is 100% recyclable and can be recycled repeatedly without degrading its inherent value. It is estimated that 75% of the aluminium which has been extracted in the last 100 years is still in use. It is indeed a rigid, long-lasting material with many practical applications, but its quality makes it very sustainable and simultaneously the culprit behind its longevity between us; an infinite life cycle.
Did you know that 1 billion tonnes of aluminium have been produced since 1886, and ¾ parts of this metal are still in use today?



Responses






