

The United States in 2024 further solidified its position as the world's largest economy, with resilient consumer spending driving its continued lead over China for the third consecutive year—at least by one key measure. According to data released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis on January 30, 2025, US GDP grew by 5.3 per cent in 2024 before adjusting for inflation. In contrast, China's nominal GDP expanded by 4.2 per cent, as reported by the country's National Bureau of Statistics a few days back.
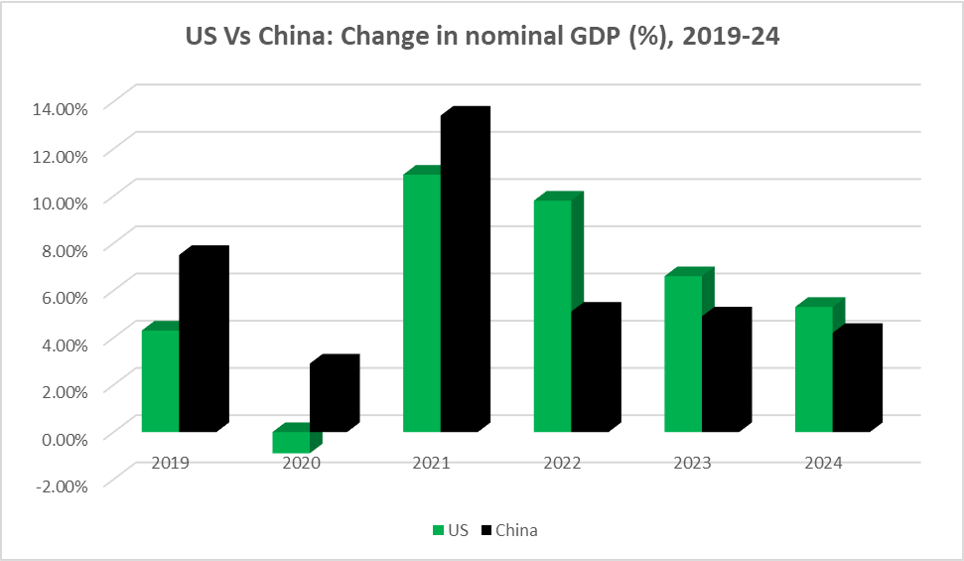
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
Note: Annual GDP, unadjusted for price changes
Nominal Gross Domestic Product (Nominal GDP) represents the total market value of all goods and services produced within a country's economy during a specific period. Unlike other GDP measurements, Nominal GDP is not adjusted for inflation or deflation, meaning it fluctuates based on changes in both economic output and price levels. As a result, nominal GDP tends to rise over time, reflecting both increased production and rising prices. In practice, Nominal GDP is often used to compare economic output to other variables, such as national debt, that are not adjusted for inflation.
The widening gap between the GDP levels of the US and China can be partly explained by their differing price challenges in recent years. In the US, inflation rates soared, leading to the Federal Reserve’s aggressive monetary tightening in 2022 and 2023, which has inflated its GDP figures. On the other hand, China has been grappling with deflation, as indicated by its GDP deflator showing a decline in prices since mid-2023.
 Events
Events
 e-Magazines
e-Magazines
 Reports
Reports



Responses






